The Future of Web Development
by Artur Szabo, Co-Founder & Full Stack Developer
1. AI-Powered Development
With tools like GitHub Copilot, ChatGPT, Grok and other tools evolving rapidly, we continue to witness the rise of AI as a core ally for developers. These AI assistants now go beyond simply suggesting code—they’re capable of debugging, optimizing, and even generating entire feature implementations. The industry has taken a significant leap toward making complex development faster and more accessible.

AI-assisted development is reshaping workflows, allowing developers to focus on innovation while delegating repetitive or tedious tasks to AI. As a result, platforms like MDN and Stack Overflow are evolving to include AI-generated explanations, while new tools like Prompt Engineer Pro are enabling developers to refine their AI instructions for better results.
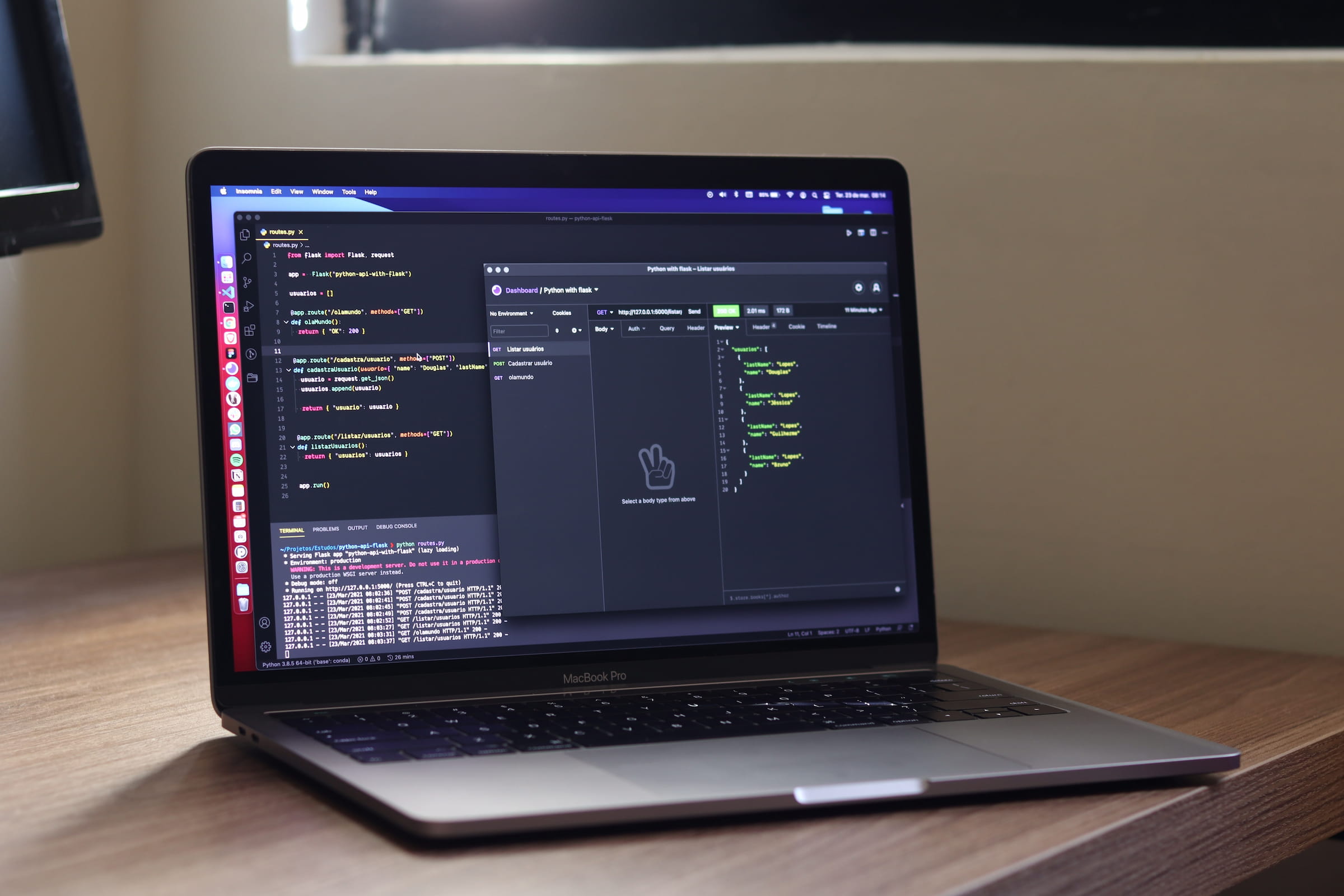
2. Rendering Innovations
Rendering approaches continue to dominate conversations in front-end development. Server-side rendering (SSR) and progressive hydration have become foundational to building highly interactive, scalable applications. Frameworks like Next.js and Astro have introduced incremental rendering, allowing components to load dynamically based on user interactions.

The year also brings more granular control over rendering strategies, with per-component rendering emerging as a standard. This ensures better performance and adaptability across varying network conditions, making user experiences seamless no matter where they’re accessing content. As the demand for Rendering Engineers rises, developers are encouraged to upskill and embrace this dynamic evolution.
3. Hyper Personalized User Experiences
The demand for personalized digital experiences has grown significantly, pushing developers to create applications that adapt dynamically to individual user preferences, behaviors, and needs. Leveraging advancements in AI and data analytics, modern applications can now deliver tailored content, recommendations, and interactions that resonate on a personal level.
From e-commerce platforms offering curated product recommendations to educational tools that adjust content delivery to different learning styles, personalization is no longer optional—it’s expected. Developers are incorporating AI-driven recommendation engines, dynamic content rendering, and behavior-based design systems to build applications that feel intuitive and engaging.
As privacy regulations tighten, there is also a shift toward privacy-first personalization, where data is processed locally or anonymized to ensure compliance while maintaining a high level of customization. Applications that prioritize both personalization and data security stand out as user trust becomes a critical differentiator in the digital space.